Bone fractures are among the most common orthopedic injuries that can affect people of all ages. They occur when the bone breaks partially or completely due to trauma, accidents, falls, or medical conditions like osteoporosis. Understanding the different types of bone fractures and their treatment options helps ensure faster recovery and prevents long-term complications.
1. What Is a Bone Fracture?
A bone fracture occurs when the normal continuity of a bone is disrupted. This may result from a direct impact, overuse, or weakening of the bone structure. Fractures can range from simple cracks to complete breaks that pierce the skin. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to restore bone strength and mobility.
2. Common Types of Bone Fractures
a) Simple (Closed) Fracture
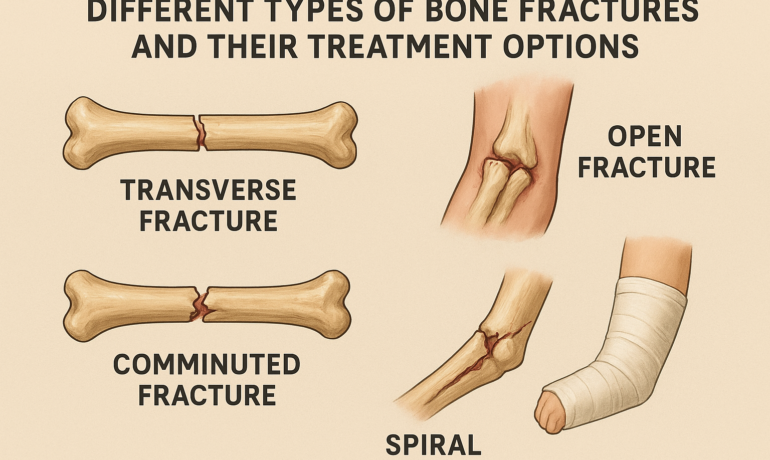
In this type, the bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin. It is less severe but still requires immediate medical attention to ensure proper alignment and healing.
b) Compound (Open) Fracture
Here, the broken bone pierces through the skin, increasing the risk of infection. This type requires urgent surgical cleaning and stabilization.
c) Greenstick Fracture
Common in children, the bone bends and cracks but doesn’t completely break. It occurs due to the flexibility of young bones and usually heals faster with immobilization.
d) Comminuted Fracture
The bone shatters into three or more pieces. High-impact injuries like car accidents are common causes, and surgery is often necessary to realign and stabilize the bone fragments.
e) Stress Fracture
A stress fracture develops from repetitive strain or overuse, especially in athletes. Rest and physical therapy are the primary treatments for this condition.
f) Pathological Fracture
These fractures occur when bones are weakened by diseases such as osteoporosis or cancer, leading to breaks even with minor stress.
3. Diagnostic Methods for Bone Fractures
Doctors use several diagnostic tools such as:
X-rays – To identify the exact location and type of fracture.
CT Scans or MRI – To detect complex or hidden fractures.
Physical Examination – To assess swelling, deformity, and range of motion.
4. Treatment Options for Bone Fractures
a) Immobilization
Casts, splints, or braces keep the bone in position to promote natural healing.
b) Traction
Used to align bones through gentle pulling. It helps in reducing pain and restoring bone position.
c) Surgical Treatment (Open Reduction and Internal Fixation)
In severe fractures, surgeons use metal plates, rods, or screws to stabilize the bone until it heals completely.
d) Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
After immobilization or surgery, physiotherapy restores strength, mobility, and function to the injured area.
5. Recovery and Prevention Tips
Eat a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
Avoid smoking and alcohol during recovery.
Follow your doctor’s rehabilitation plan strictly.
Engage in weight-bearing exercises to improve bone density.
Conclusion
Timely diagnosis and the right treatment approach are crucial for effective bone fracture recovery. Proper care helps prevent complications and ensures long-term mobility.
If you suspect a fracture, don’t delay medical attention — early intervention ensures faster healing and better outcomes.Dr. Aditya Somayaji – Ortho Best Orthopedic Surgeon in Kondapur.